MEMS based Ring Laser Gyroscope with Reduced Lock-in
Description
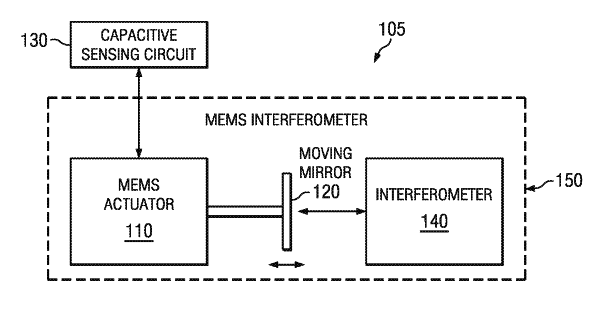
Embodiments of the present invention provide a ring laser gyroscope including an active gain medium for generating first and second light beams, a closed optical path through which the first and second light beams counter-propagate, first and second moveable mirrors within the closed optical path and a Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) actuator coupled to the first and second moveable minors to cause a respective displacement thereof that induces a phase modulation on the first and second light beams relative to one another, thereby creating an optical path difference between the first and second light beams corresponding to a virtual rotation to reduce the lock-in. In one embodiment, the active gain medium includes a semiconductor laser. In another embodiment, the active gain medium includes a fiber amplifier. In either embodiment, the first and second mirrors may be metallic or dielectric and may be moveable in the same direction or in opposite directions. In addition, a single MEMS actuator may control both the first and second minors or each mirror may be separately controlled by a different MEMS actuator. In a further embodiment, one or more additional mirrors may be placed in the closed optical path to direct the light beams. In such an embodiment, the first and second minors may be corner cube minors. In still a further embodiment, the first and second mirrors and the MEMS actuator may be fabricated on a silicon on insulator (SOI) wafer. The active gain medium may be further fabricated on the SOI wafer or on a separate SOI wafer. When the active gain medium is fabricated on a separate SOI wafer, the closed optical path may further include an optical fiber coupled between the two SOI wafers. In yet another embodiment, the RLG further includes a detector coupled to the closed optical path to detect a beat pattern caused by the first and second light beams counter-propagating through the closed optical path and a processor coupled to the detector to determine an angular rotation rate based on the beat pattern. In an exemplary embodiment, a mirror that is at least partially transmissive within the closed optical path directs the first and second light beams towards the detector. In another exemplary embodiment, a coupler within the closed optical path splits the first and second light beams such that the first light beam propagates in a first direction in the coupler and the second light beam propagates in a second direction in the coupler and then recombines the first and second light beams at the detector to create an interference pattern thereon. For example, the coupler may include one or more of an optical fiber coupler, a prism coupler and a directional coupler.
Aspects
Ring laser gyroscopes (RLGs) are instruments that measure the angular rotation rate of a certain platform. An RLG typically includes a laser system designed and fabricated to work in a ring configuration. The most familiar form of an RLG is built using a helium-neon (HN) ring laser with a diameter in the range of 30 cm. The present invention relates in general to ring laser gyroscope designs, and in particular to the use of Micro Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) technology in ring laser gyroscope designs.
Patenting Status
Patent Granted
Submit Your Intellectual Property Send Your Feedback




























































EgyptInnovate site is not responsible for the content of the comments